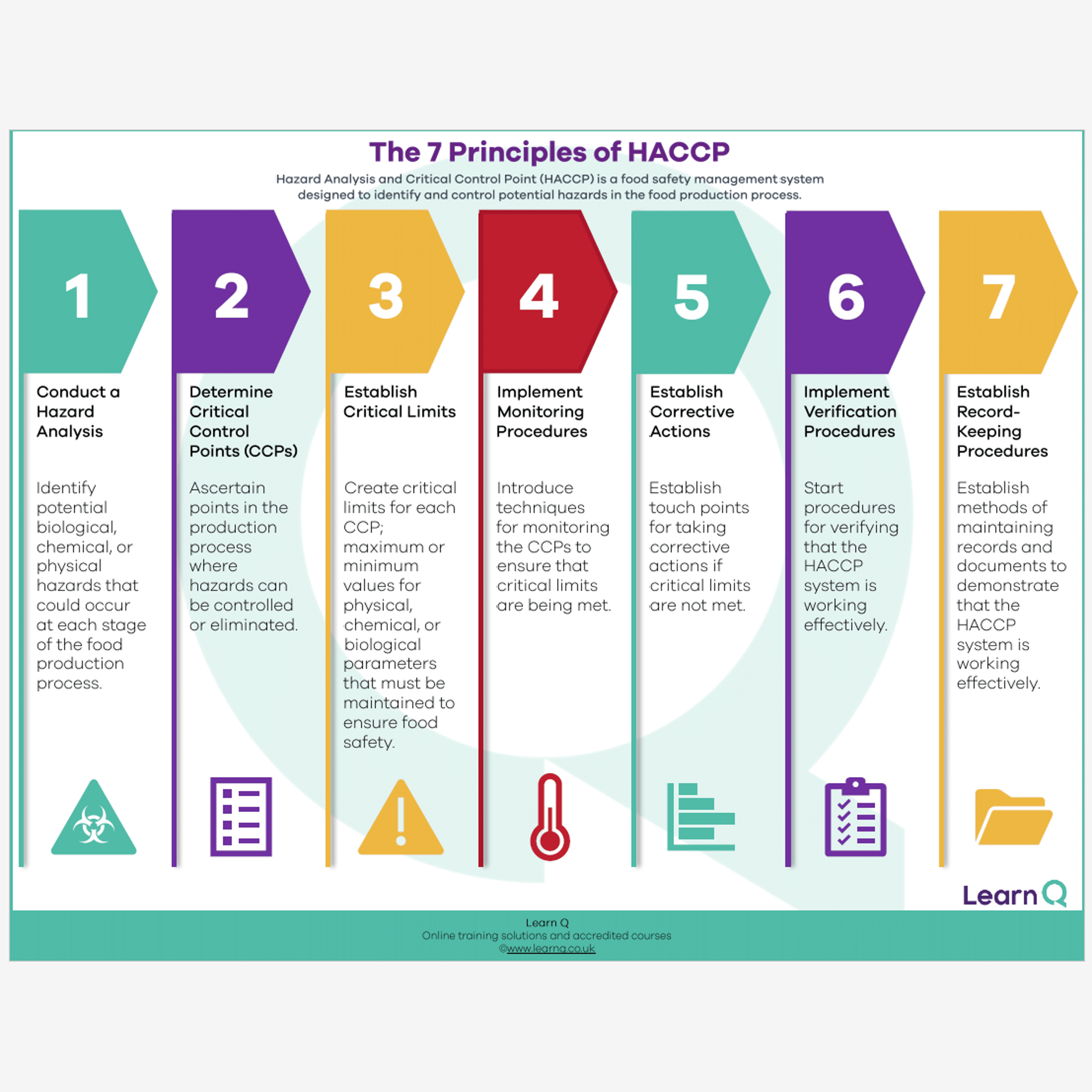
HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) is a systematic approach to ensuring food safety. Developed in the 1960s by a team of scientists and engineers for NASA’s space program, HACCP has since become a cornerstone of modern food safety management.
It emphasises the identification, assessment, and control of potential hazards in the food production process. The seven principles of HACCP provide a comprehensive framework to safeguard food from farm to table.
Click here to download a FREE Principles of HACCP Poster, and read on to learn more:
- Conduct a Hazard Analysis:
The first principle involves identifying potential biological, chemical, or physical hazards that could compromise food safety. This analysis serves as the foundation for the rest of the HACCP process, allowing for a thorough understanding of risks specific to the food production process.
- Determine Critical Control Points (CCPs):
CCPs are specific points in the production process where control can be exerted to prevent, eliminate, or reduce identified hazards to acceptable levels. These points are pivotal in ensuring that food safety risks are effectively managed.
- Establish Critical Limits:
Critical limits are predetermined parameters that must be met at each CCP to ensure food safety. These limits could relate to temperature, time, pH levels, moisture, or other relevant factors. They act as benchmarks for gauging whether a process is under control.
- Implement Monitoring Procedures:
Monitoring involves regular checks to ensure that CCPs are operating within established critical limits. This ongoing oversight helps detect any deviations from the norm, allowing for timely corrective action to prevent food safety hazards from occurring.
- Develop Corrective Actions:
When deviations from critical limits are identified, corrective actions are necessary. These actions detail the steps to bring the process back under control and mitigate the potential food safety hazard. The goal is to quickly address and rectify any issues to prevent contaminated products from reaching consumers.
- Establish Verification Procedures:
Verification involves periodic reviews and validations of the HACCP system’s effectiveness. This ensures that the system remains robust and continues to provide the intended level of food safety. External audits, inspections, and testing are common verification methods.
- Create a Record-Keeping System:
Maintaining accurate records is crucial to HACCP’s success. Records track various aspects of the process, including hazard analysis, CCP monitoring, corrective actions, and verification procedures. These records serve as evidence of compliance and provide a historical perspective for continuous improvement.
If you want a structured way to improve your HACCP practices, you could take a course with Learn Q. Click here to learn more.